Oracle provides following methods to convert a single instance database to RAC. You can choose any method based upon your convince.
1. Manual (Using RMAN)
2. Enterprise Manager
3. DBCA
4. RCONFIG (from 10gR2)
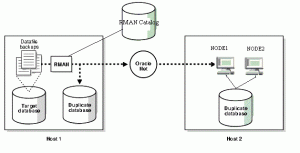
Duplicating RAC database is very simple, first duplicate RAC Database to a single instance using RMAN and convert the single instance into a RAC cluster. Please note that straight RAC to RAC duplicate is not possible.
Follow the simple steps to duplicate RAC Database using ASM or other filesystem.
Step1: Create a parameter file for duplicate database(auxiliary)
The easy ways is copy Init.ora parameter from Target database, replace the Target database name with Auxiliary database name and comment all RAC related parameters for ex:- cluster_database, cluster_instances, thread …Etc
Set CONTROL_FILES to two copies of the control file to +DISKGRP or file system
Step 2: Set DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT and LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT to convert the datafile and redo log file names from +DISKGRP1 to +DISKGRP2 or /dbs1 to /dbs2 (For Non-ASM file systems)
Also Set DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST and DB_CREATE_ONLINE_DEST_n to ‘+DISKGRP2’ or /dbs2
Step 3: set _no_recovery_through_resetlogs=TRUE parameter to avoid internal Bug 4355382 ORA-38856: FAILED TO OPEN DATABASE WITH RESETLOGS WHEN USING RAC BACKUP
Step 4: Create a password file for auxiliary database using below command.
$ orapwd file=orapwdupDB password=xxxxxxxx
Step 5: Create a static listener for auxiliary database and reload, because auxiliary database will not register itself with the listener.
(SID_DESC =
(GLOBAL_DBNAME =dupDB.oracleracexpert.com)
(ORACLE_HOME = /oracle/product/db/10202)
(SID_NAME = dupDB)
)
Step 6: Take Full database backup of Target database
RMAN > backup database plus archivelog;
Copy the backup dumps from Target to Auxiliary host. If backup directory structure is different then update the RMAN configuration of the target database to reflect the new backup location
RMAN> CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT ‘/oracle/rman/dupDB’;
Step7: Set ORACLE_SID and start auxiliary database in NO MOUNT state
$ export ORACLE_SID=dupDB
SQL> startup nomount
Step 8: Duplicate Target Database using RMAN Duplicate command
RMAN> CONNECT TARGET /;
RMAN> CONNECT CATALOG rman/*****@catadb;
RMAN> CONNECT AUXILIARY sys/*****@dupDB;
RMAN> DUPLICATE TARGET DATABASE TO dupDB;
Step 9: Add second thread of online redo logs and enable that thread:
SQL> alter database add logfile thread 2
group 3 (‘+DISKGRP1′,’+DISKGRP2’) size 50m reuse;
SQL> alter database add logfile thread 2
group 4 (‘+DISKGRP1′,’+DISKGRP2′) size 50m reuse;
SQL> alter database enable public thread 2;
For Non-ASM file systems replace ‘+DISKGRP1’, ‘+DISKGRP2’ with actual file systems path
Step 10: Uncomment or add all RAC related parameters, shutdown the instance and startup both Instances.
Step 11: create spfile on the shared storage, because all instances must use the same server parameter file. See the link to “Create spfile from pfile”.
Step12: Register RAC instances with CRS
$ srvctl add database -d dupDB -o /oracle/product/db/10202
$ srvctl add instance -d dupDB -i dupDB1 -n testrac01
$ srvctl add instance -d dupDB -i dupDB2 -n testrac02
Step13: Shutdown and startup instances using srvctl
$ srvctl start database –d dupDB
Src: Satishbabu Gunukula
http://www.oracleracexpert.com/